2024 United States presidential election: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| votes_for_election = 538 members of the [[w:United States Electoral College|Electoral College]] | | votes_for_election = 538 members of the [[w:United States Electoral College|Electoral College]] | ||
| needed_votes = 270 electoral | | needed_votes = 270 electoral | ||
| turnout = | | turnout = 62.7% ({{decrease}} 4.2 [[percentage point|pp]]) | ||
| map_image = {{2024 United States presidential election imagemap}} | | map_image = {{2024 United States presidential election imagemap}} | ||
| map_size = | | map_size = | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| home_state1 = [[w:California|California]] | | home_state1 = [[w:California|California]] | ||
| running_mate1 = '''[[w:Tim Walz|Tim Walz]]''' | | running_mate1 = '''[[w:Tim Walz|Tim Walz]]''' | ||
| electoral_vote1 = ''' | | electoral_vote1 = '''303''' | ||
| states_carried1 = ''' | | states_carried1 = '''25 + [[w:Washington, D.C.|DC]] + {{ushr|w:NE|2|NE-02}}''' | ||
| popular_vote1 = ''' | | popular_vote1 = '''80,482,976''' | ||
| percentage1 = ''' | | percentage1 = '''51.2%''' | ||
| | | | ||
| image2 = TrumpPortrait (3x4a).jpg | | image2 = TrumpPortrait (3x4a).jpg | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
| home_state2 = [[w:Florida|Florida]] | | home_state2 = [[w:Florida|Florida]] | ||
| running_mate2 = [[w:JD Vance|JD Vance]] | | running_mate2 = [[w:JD Vance|JD Vance]] | ||
| electoral_vote2 = | | electoral_vote2 = 235 | ||
| states_carried2 = | | states_carried2 = 25 + {{ushr|w:ME|2|ME-02}} | ||
| popular_vote2 = | | popular_vote2 = 74,481,957 | ||
| percentage2 = | | percentage2 = 47.4% | ||
| | | | ||
| map_caption = Presidential election results map. <span style="color:darkred;">Red</span> denotes [[w:U.S. states|U.S. states]] won by Trump/Vance and <span style="color:darkblue">blue</span> denotes those won by Harris/Walz. Numbers indicate [[w:United States Electoral College|electoral votes]] cast by each state and the [[w:District of Columbia|District of Columbia]]. | | map_caption = Presidential election results map. <span style="color:darkred;">Red</span> denotes [[w:U.S. states|U.S. states]] won by Trump/Vance and <span style="color:darkblue">blue</span> denotes those won by Harris/Walz. Numbers indicate [[w:United States Electoral College|electoral votes]] cast by each state and the [[w:District of Columbia|District of Columbia]]. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[United States presidential election|Presidential elections]] were held in the [[United States]] on November 5, 2024. The [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]]'s [[Ticket (election)|ticket]]—[[Kamala Harris]], the incumbent [[U.S. vice president]], and [[Tim Walz]], the incumbent [[governor of Minnesota]]—defeated the [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican Party]]'s ticket—[[Donald Trump]], who served as the 45th [[president of the United States]] from 2017 to 2021, and [[JD Vance]], a [[U.S. senator]] from [[Ohio]]. | [[w:United States presidential election|Presidential elections]] were held in the [[United States]] on November 5, 2024. The [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]]'s [[w:Ticket (election)|ticket]]—[[w:Kamala Harris|Kamala Harris]], the incumbent [[w:U.S. vice president|U.S. vice president]], and [[w:Tim Walz|Tim Walz]], the incumbent [[w:governor of Minnesota|governor of Minnesota]]—defeated the [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican Party]]'s ticket—[[w:Donald Trump|Donald Trump]], who served as the 45th [[w:president of the United States|president of the United States]] from 2017 to 2021, and [[w:JD Vance|JD Vance]], a [[w:U.S. senator|U.S. senator]] from [[w:Ohio|Ohio]]. | ||
The incumbent president, Democrat [[Joe Biden]], initially [[Joe Biden 2024 presidential campaign|ran for re-election]] as the party's [[presumptive nominee]], facing little opposition and easily defeating Representative [[Dean Phillips]] of [[Minnesota]] during the [[2024 Democratic Party presidential primaries|Democratic primaries]]; however, what was broadly considered a [[2024 Joe Biden–Donald Trump presidential debate|poor debate performance]] in June 2024 intensified [[Age and health concerns about Joe Biden|concerns about his age and health]], and led to [[List of Democrats who opposed the Joe Biden 2024 presidential campaign|calls within his party]] for him to leave the race. After initially declining to do so, [[Withdrawal of Joe Biden from the 2024 United States presidential election|Biden withdrew]] on July 21, becoming the first eligible incumbent president to withdraw since [[Withdrawal of Lyndon B. Johnson from the 1968 United States presidential election|Lyndon B. Johnson in 1968]]. Biden endorsed Harris, who was voted [[Kamala Harris 2024 presidential campaign|the party's nominee]] by the delegates on August 5 and became the first nominee who did not participate in the [[United States presidential primary|primaries]] since [[Hubert Humphrey 1968 presidential campaign|Hubert Humphrey, also in 1968]]. Harris [[2024 Democratic Party vice presidential candidate selection|selected Walz as her running mate]]. | The incumbent president, Democrat [[w:Joe Biden|Joe Biden]], initially [[w:Joe Biden 2024 presidential campaign|ran for re-election]] as the party's [[w:presumptive nominee|presumptive nominee]], facing little opposition and easily defeating Representative [[w:Dean Phillips|Dean Phillips]] of [[w:Minnesota|Minnesota]] during the [[w:2024 Democratic Party presidential primaries|Democratic primaries]]; however, what was broadly considered a [[w:2024 Joe Biden–Donald Trump presidential debate|poor debate performance]] in June 2024 intensified [[w:Age and health concerns about Joe Biden|concerns about his age and health]], and led to [[w:List of Democrats who opposed the Joe Biden 2024 presidential campaign|calls within his party]] for him to leave the race. After initially declining to do so, [[w:Withdrawal of Joe Biden from the 2024 United States presidential election|Biden withdrew]] on July 21, becoming the first eligible incumbent president to withdraw since [[w:Withdrawal of Lyndon B. Johnson from the 1968 United States presidential election|Lyndon B. Johnson in 1968]]. Biden endorsed Harris, who was voted [[w:Kamala Harris 2024 presidential campaign|the party's nominee]] by the delegates on August 5 and became the first nominee who did not participate in the [[w:United States presidential primary|primaries]] since [[w:Hubert Humphrey 1968 presidential campaign|Hubert Humphrey, also in 1968]]. Harris [[w:2024 Democratic Party vice presidential candidate selection|selected Walz as her running mate]]. | ||
Trump, who lost [[2020 United States presidential election|the 2020 presidential election]] to Biden, [[Donald Trump 2024 presidential campaign|ran for reelection]] to a nonconsecutive second term. He was shot in the ear in [[Attempted assassination of Donald Trump in Pennsylvania|an assassination attempt]] on July 13, 2024. Trump was nominated as the Republican Party's presidential candidate during the [[2024 Republican National Convention]] alongside his running mate, Vance. [[Donald Trump 2024 presidential campaign|The Trump campaign]] ticket supported mass deportation of undocumented immigrants; | Trump, who lost [[w:2020 United States presidential election|the 2020 presidential election]] to Biden, [[w:Donald Trump 2024 presidential campaign|ran for reelection]] to a nonconsecutive second term. He was shot in the ear in [[w:Attempted assassination of Donald Trump in Pennsylvania|an assassination attempt]] on July 13, 2024. Trump was nominated as the Republican Party's presidential candidate during the [[w:2024 Republican National Convention|2024 Republican National Convention]] alongside his running mate, Vance. [[w:Donald Trump 2024 presidential campaign|The Trump campaign]] ticket supported mass deportation of undocumented immigrants; an [[w:isolationism|isolationist]] "[[w:America First|America First]]" foreign policy agenda with support of Israel in the [[w:Gaza war|Gaza war]] and skepticism of Ukraine in its [[w:Russian invasion of Ukraine|war with Russia]]; [[w:Transphobia in the United States|anti-transgender policies]]; and [[w:Tariffs in the second Trump administration|tariffs]]. The campaign also made [[w:False or misleading statements by Donald Trump|false and misleading statements]], including [[w:False claims of fraud in the 2020 presidential election|claims of electoral fraud in 2020]]. [[w:Trumpism|Trump's political movement]] was seen by some historians and some former [[w:First cabinet of Donald Trump|Trump administrators]] as [[w:authoritarian|authoritarian]]. | ||
Harris won the [[United States Electoral College|Electoral College]] with 303 electoral votes to Trump's 235. She carried every state that Biden won in 2020, including the critical battlegrounds of [[2024 United States presidential election in Michigan|Michigan]], [[2024 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania|Pennsylvania]], [[2024 United States presidential election in Wisconsin|Wisconsin]], [[2024 United States presidential election in Arizona|Arizona]], [[2024 United States presidential election in Georgia|Georgia]], and [[2024 United States presidential election in Nevada|Nevada]]. She also won [[2024 United States presidential election in Nebraska|Nebraska's 2nd congressional district]], which had been a key target for both campaigns. Harris lost [[2024 United States presidential election in North Carolina|North Carolina]] and [[2024 United States presidential election in Florida|Florida]] by narrow margins. She became the first woman and first Asian American to be elected president of the United States. Harris won the national [[List of United States presidential elections by popular vote margin|popular vote]] with 51.2%, defeating Trump by a margin of approximately | Harris won the [[w:United States Electoral College|Electoral College]] with 303 electoral votes to Trump's 235. She carried every state that Biden won in 2020, including the critical battlegrounds of [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Michigan|Michigan]], [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania|Pennsylvania]], [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Wisconsin|Wisconsin]], [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Arizona|Arizona]], [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Georgia|Georgia]], and [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Nevada|Nevada]]. She also won [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Nebraska|Nebraska's 2nd congressional district]], which had been a key target for both campaigns. Harris lost [[w:2024 United States presidential election in North Carolina|North Carolina]] and [[w:2024 United States presidential election in Florida|Florida]] by narrow margins. She became the first woman and first Asian American to be elected president of the United States. Harris won the national [[w:List of United States presidential elections by popular vote margin|popular vote]] with 51.2%, defeating Trump by a margin of approximately 5.5 million votes. Analysts credited Harris's victory to high Democratic turnout, broad suburban support, and improved margins among women and young voters. | ||
== Background == | |||
{{further|w:United States presidential election#Procedure}} | |||
[[File:Absentee Ballot, 2024.jpg|thumb|A general election absentee ballot from [[W:Fairfax County, Virginia|Fairfax County, Virginia]], listing the presidential and vice presidential candidates]] | |||
[[File:Joe Biden presidential portrait.jpg|thumb|upright|The [[w:incumbent|incumbent]] in 2024, [[w:Joe Biden|Joe Biden]]. His term expired at noon on January 20, 2025.]] | |||
In 2020, incumbent Republican President Donald Trump was defeated by Democratic challenger Joe Biden. Democratic U.S. Senator Kamala Harris of California was elected vice president as Biden’s running mate. | |||
Trump was the first president in U.S. history to be [[w:Efforts to impeach Donald Trump|impeached twice]], and the first to seek re-election following impeachment. As he was acquitted by the Senate in both cases, he remained eligible to run in 2024. | |||
=== Election interference === | |||
{{main|w:Election interference}} | |||
{{further|w:Republican efforts to restrict voting following the 2020 presidential election|w:Attempts to overturn the 2020 United States presidential election|w:January 6 United States Capitol attack|w:Presidential eligibility of Donald Trump}} | |||
In the run-up to the 2024 election, several state officials and courts attempted to disqualify Trump from the ballot under Section 3 of the [[w:Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution]], citing his role in the January 6 Capitol attack. These included the [[w:Colorado Supreme Court|Colorado Supreme Court]], a Circuit Court in [[w:Illinois|Illinois]], and the [[w:Secretary of State of Maine|Secretary of State of Maine]]. | |||
On March 4, 2024, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled unanimously in ''[[w:Trump v. Anderson|Trump v. Anderson]]'' that states lacked the authority to enforce Section 3 for federal candidates without congressional legislation, allowing Trump to remain on the ballot nationwide. | |||
==== Donald Trump's false claims of interference ==== | |||
{{further|w:Big lie#Donald Trump's false claims of a stolen election|w:Election denial movement in the United States|w:Republican Party efforts to disrupt the 2024 United States presidential election}} | |||
[[File:20240524 Trump groundwork for election denial.svg|thumb|200x200px|Trump increased the use of "rigged election" and "election interference" rhetoric before the 2024 election.]] | |||
Trump repeatedly claimed without evidence that the 2024 election would be rigged, continuing rhetoric similar to his false claims following the 2020 election. | |||
''The New York Times'' reported in July 2024 that the Republican Party and aligned groups were preparing a broad legal campaign aimed at challenging election processes and results, including limiting voting access in key states and preparing to dispute certification should Trump lose. | |||
The Republican Party also promoted baseless claims of noncitizen voting, while Trump and others refused to commit to accepting the 2024 results if they believed the outcome was "unfair". | |||
Trump also reignited concerns about democratic erosion in the U.S. through his statements suggesting he could suspend the Constitution, his pledge to act as a "dictator" on "day one", and his plans to weaponize the Justice Department and invoke the [[w:Insurrection Act of 1807|Insurrection Act of 1807]] against Democratic jurisdictions. | |||
Observers warned that Trump’s actions and rhetoric posed a threat to U.S. democracy, with election deniers gaining ground within the Republican Party and plans to monitor polling places intensifying across battleground states. | |||
Latest revision as of 21:25, 4 August 2025
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 62.7% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
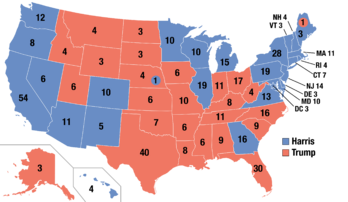 Presidential election results map. Red denotes U.S. states won by Trump/Vance and blue denotes those won by Harris/Walz. Numbers indicate electoral votes cast by each state and the District of Columbia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 5, 2024. The Democratic Party's ticket—Kamala Harris, the incumbent U.S. vice president, and Tim Walz, the incumbent governor of Minnesota—defeated the Republican Party's ticket—Donald Trump, who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021, and JD Vance, a U.S. senator from Ohio.
The incumbent president, Democrat Joe Biden, initially ran for re-election as the party's presumptive nominee, facing little opposition and easily defeating Representative Dean Phillips of Minnesota during the Democratic primaries; however, what was broadly considered a poor debate performance in June 2024 intensified concerns about his age and health, and led to calls within his party for him to leave the race. After initially declining to do so, Biden withdrew on July 21, becoming the first eligible incumbent president to withdraw since Lyndon B. Johnson in 1968. Biden endorsed Harris, who was voted the party's nominee by the delegates on August 5 and became the first nominee who did not participate in the primaries since Hubert Humphrey, also in 1968. Harris selected Walz as her running mate.
Trump, who lost the 2020 presidential election to Biden, ran for reelection to a nonconsecutive second term. He was shot in the ear in an assassination attempt on July 13, 2024. Trump was nominated as the Republican Party's presidential candidate during the 2024 Republican National Convention alongside his running mate, Vance. The Trump campaign ticket supported mass deportation of undocumented immigrants; an isolationist "America First" foreign policy agenda with support of Israel in the Gaza war and skepticism of Ukraine in its war with Russia; anti-transgender policies; and tariffs. The campaign also made false and misleading statements, including claims of electoral fraud in 2020. Trump's political movement was seen by some historians and some former Trump administrators as authoritarian.
Harris won the Electoral College with 303 electoral votes to Trump's 235. She carried every state that Biden won in 2020, including the critical battlegrounds of Michigan, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, Arizona, Georgia, and Nevada. She also won Nebraska's 2nd congressional district, which had been a key target for both campaigns. Harris lost North Carolina and Florida by narrow margins. She became the first woman and first Asian American to be elected president of the United States. Harris won the national popular vote with 51.2%, defeating Trump by a margin of approximately 5.5 million votes. Analysts credited Harris's victory to high Democratic turnout, broad suburban support, and improved margins among women and young voters.
Background


In 2020, incumbent Republican President Donald Trump was defeated by Democratic challenger Joe Biden. Democratic U.S. Senator Kamala Harris of California was elected vice president as Biden’s running mate.
Trump was the first president in U.S. history to be impeached twice, and the first to seek re-election following impeachment. As he was acquitted by the Senate in both cases, he remained eligible to run in 2024.
Election interference
In the run-up to the 2024 election, several state officials and courts attempted to disqualify Trump from the ballot under Section 3 of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, citing his role in the January 6 Capitol attack. These included the Colorado Supreme Court, a Circuit Court in Illinois, and the Secretary of State of Maine.
On March 4, 2024, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled unanimously in Trump v. Anderson that states lacked the authority to enforce Section 3 for federal candidates without congressional legislation, allowing Trump to remain on the ballot nationwide.
Donald Trump's false claims of interference

Trump repeatedly claimed without evidence that the 2024 election would be rigged, continuing rhetoric similar to his false claims following the 2020 election.
The New York Times reported in July 2024 that the Republican Party and aligned groups were preparing a broad legal campaign aimed at challenging election processes and results, including limiting voting access in key states and preparing to dispute certification should Trump lose.
The Republican Party also promoted baseless claims of noncitizen voting, while Trump and others refused to commit to accepting the 2024 results if they believed the outcome was "unfair".
Trump also reignited concerns about democratic erosion in the U.S. through his statements suggesting he could suspend the Constitution, his pledge to act as a "dictator" on "day one", and his plans to weaponize the Justice Department and invoke the Insurrection Act of 1807 against Democratic jurisdictions.
Observers warned that Trump’s actions and rhetoric posed a threat to U.S. democracy, with election deniers gaining ground within the Republican Party and plans to monitor polling places intensifying across battleground states.

